Economía Circular y ACV
Ayudamos a traducir la economía circular a la realidad de su negocio.
Asistimos a clientes para desarrollar su estrategia de economía circular asesorando en la eliminación, reducción y mejora de tratamientos para sus residuos principales
En EHS Techniques contamos con experiencia en el sector farmacéutico, manufactura, alimentario y EDAR.
Además, ayudamos a transformar el modelo de negocio de su empresa para alinearlo con los principios de la economía circular gracias al Análisis de Ciclo de Vida (ACV), una herramienta que permite evaluar los impactos ambientales de productos y servicios a lo largo de todo su ciclo de vida. Acompañamos y guiamos a empresas para identificar puntos críticos en la cadena de valor, optimizar procesos, cumplir con normativas y certificaciones ambientales y diseñar estrategias para potenciar la circularidad y la sostenibilidad de su negocio. Nuestro enfoque combina estrategia, técnica y compromiso, para que las prácticas sostenibles sean rentables y generadoras de valor a medio y largo plazo.
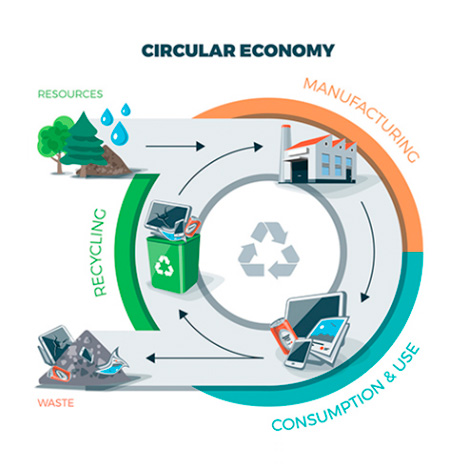
¿Qué es la economía circular?
La economía circular es un modelo innovador de producción y consumo en el que se maximiza el valor de los productos y los recursos, en el que minimiza la generación de residuos y en el que se aprovechan al máximo los residuos que no se pueden evitar. Se trata de desvincular el crecimiento económico del consumo de recursos y constituye, además, una contribución esencial a los esfuerzos de la Unión Europea para alcanzar una economía sostenible, descarbonizada, eficiente y competitiva. En lugar del modelo lineal (“tomar-fabricar-consumir-eliminar”), la economía circular busca:
- Reducir y eliminar residuos: el objetivo es minimizar la generación de residuos y aprovechar aquellos cuya generación no se haya podido evitar.
- Mantener el valor de los productos y materiales: se centra en extender la vida útil de los productos a través de la reutilización, la reparación y el reciclaje.
- Maximizar la eficiencia de los recursos: rediseñar productos y procesos productivos para utilizar los recursos (agua, energía, materiales) de manera más eficiente, reduciendo la necesidad de extraer nuevas materias primas.
- Desvincular el crecimiento económico del consumo de recursos: al transformar los “residuos” en “recursos”, la economía circular permite que la economía crezca sin agotar los recursos naturales finitos.
- Fomentar la regeneración de sistemas naturales: se basa en ralentizar el uso de recursos naturales, lo que limita la pérdida de biodiversidad y reduce las emisiones a la atmósfera, al agua y al suelo.
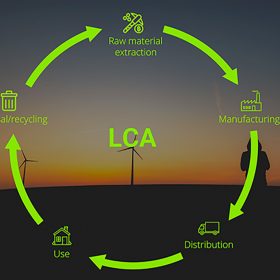
¿Qué es el Análisis de Ciclo de Vida (ACV)?
El ACV es una herramienta esencial para el análisis de la sostenibilidad que ayuda a comprender el impacto ambiental de todos los productos o servicios. Al considerar el ciclo completo, desde la extracción de materias primas hasta la disposición final de los residuos, el ACV ofrece una visión holística que ayuda a identificar áreas de mejora y a promover prácticas más sostenibles. Los resultados permiten identificar la contribución del producto o servicio a, por ejemplo, el calentamiento global (huella de carbono), la acidificación de la atmósfera, la eutrofización de las aguas, la ecotoxicidad, el consumo de agua, agotamiento de recursos, etc., identificando así los puntos críticos y permitiendo establecer estrategias de mejora.
Nuestro método en EHS Techniques
Para acompañar a su empresa en esta transición, nuestro proceso se estructura en 4 fases:
- Definición de estrategia circular: Analizamos sus actividades, productos y cadena de suministro. Establecemos objetivos medibles y alcanzables en economía circular, reducción de residuos, ecodiseño y eficiencia de recursos.
- Evaluación de impacto ambiental mediante ACV: Realizamos estudios completos de Análisis de Ciclo de Vida, declaraciones ambientales de producto o estudios de un solo indicador, como el cálculo de huella de carbono de producto o la huella hídrica.
- Plan de acción para reducir o compensar impactos: Diseñamos hojas de ruta que incluyen mejoras prácticas, adopción de tecnologías bajas en carbono, optimización de procesos, alianzas para reciclado, eco-innovación, y medidas compensatorias cuando sea necesario.
- Seguimiento y monitorización: Implantamos indicadores clave de rendimiento (KPIs) ambientales, revisamos continuamente los objetivos, para asegurar mejora continua.
Beneficios de aplicar economía circular y ACV
- Cumplimiento legal y normativo frente a regulaciones ambientales crecientes (UE, España).
- Reducción de costes materiales, energía y residuos.
- Mejora de la reputación corporativa, imagen responsable, diferenciación sostenible.
- Acceso a ayudas, subvenciones e incentivos públicos / fondos europeos, relacionados con la transición ecológica.
- Mitigación de riesgos de cadena de suministro, dependencia de materias primas críticas, futuras restricciones de mercado.
¿Por qué EHS Techniques?
- Equipo multidisciplinar con experiencia en ingeniería química, ambiental y normativa europea.
- Estudios rigurosos basados en estándares y acompañamiento durante el proceso de verificación.
- Enfoque personalizado, adaptado al sector (industrial, productos, servicios…).
- Transparencia y compromiso con la mejora continua.
- Experiencia en el sector farmacéutico, manufactura, alimentario y EDAR.
Si desea que su empresa reduzca su impacto ambiental, optimice recursos y se prepare para los desafíos regulatorios y de mercado, contáctenos. Con EHS Techniques, la economía circular no es solo una aspiración, sino un camino hacia la competitividad y sostenibilidad real.
Economía circular y ACV • Preguntas frecuentes
La economía circular rompe con el modelo tradicional de “extraer, producir, consumir y desechar” y propone un sistema en el que los productos, materiales y recursos se mantienen en uso el mayor tiempo posible.
Para incorporar la economía circular en tu empresa y obtener un modelo de negocio más circular se pueden llevar a cabo numerosas acciones como el rediseño de productos o servicios, la colaboración con proveedores sostenibles, la obtención de certificaciones como residuos cero, declaración ambiental de producto, huella de carbono de producto, etc.
Los estudios de ACV, de acuerdo con la norma ISO 14040, se hacen siguiendo estas cuatro fases:
- Definición de objetivos y alcance: Se establece qué se quiere analizar, por qué y para qué. Se define el sistema del producto, los límites del estudio (por ejemplo, de la cuna a la tumba), y los criterios de calidad de datos.
- Análisis del inventario (LCI): Se recopilan datos sobre todos los flujos de entrada y salida del sistema: materias primas, energía, emisiones, residuos, transporte, etc. Esta fase es cuantitativa y requiere una gran cantidad de datos precisos.
- Evaluación de impacto (LCIA): Se traduce el inventario en impactos ambientales: cambio climático, acidificación, eutrofización, agotamiento de recursos, etc. Se agrupan los impactos en categorías y se valoran según su relevancia.
- Interpretación: Se analizan los resultados para extraer conclusiones útiles. Se identifican puntos críticos, se proponen mejoras y se evalúa la fiabilidad del estudio.
Algunos de los beneficios son:
- Ahorro económico: reducción de costes operativos al disminuir la dependencia de materias primas, reutilizar materiales, optimizar procesos, y reducir la producción de residuos.
- Reducción del impacto ambiental: disminución de emisiones al aire, al agua y al suelo, consumo de recursos y energía no renovables, etc. Además, se cumplen con normativas ambientales y se contribuye a los objetivos climáticos.
- Innovación: Fomento de la innovación en productos, procesos y modelos de negocio circulares.
- Reputación y fidelización: Mejora de la imagen corporativa al adoptar prácticas sostenibles y responsables.
- Nuevas oportunidades de negocio: Acceso a mercados verdes, subvenciones y financiación sostenible o Creación de nuevas líneas de ingresos a partir de residuos valorizados o productos reacondicionados
Normas para el Análisis de Ciclo de Vida (ACV)
- ISO 14040:2006 Gestión ambiental – Evaluación del ciclo de vida – Principios y marco: Define los principios generales, el marco metodológico y los límites del sistema para realizar un ACV
- ISO 14044:2006 Gestión ambiental – Evaluación del ciclo de vida – Requisitos y directrices: Establece los requisitos técnicos para llevar a cabo un ACV, incluyendo la recopilación de datos, evaluación de impactos y validación de resultados
Normas para Economía Circular
- ISO 59004:2024 Circular economy — Vocabulary, principles and guidance for implementation: Define los principios clave y proporciona orientación para aplicar la economía circular en organizaciones
La economía circular mejora la sostenibilidad y eficiencia industrial al reducir el consumo de recursos, minimizar residuos, optimizar procesos y fomentar la innovación tecnológica. Esto se traduce en ahorro económico, menor impacto ambiental y mayor resiliencia operativa.

 Español
Español